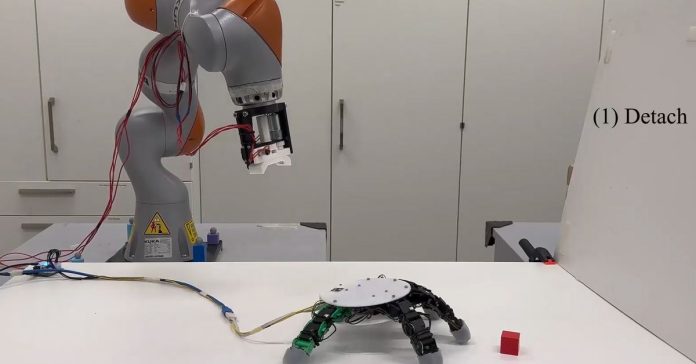
Because of their energy and velocity, robotic arms are usually completely hooked up to flooring or different buildings for added stability, which limits their attain. The aim of the analysis, carried out on the EPFL’s Studying Algorithms and Methods Laboratory (LASA), was to develop a bimodal robotic hand with expanded greedy capabilities, together with occasional independence from the robotic arm it’s hooked up to.
Robotic palms are normally designed with a single aim in thoughts: to carry onto issues. To develop one that would try this and crawl round by itself just like the Addams Household’s Factor, the researchers generated and refined a fundamental design utilizing a genetic algorithm (which depends on organic tips like pure choice and evolution) and the MuJoCo physics simulator to check the practicality of iterations.
The algorithm and simulations helped the researchers decide the optimum place and variety of articulated fingers wanted, which turned out to be 5, in an identical structure to human palms. The robotic hand additionally makes use of a magnetic connector on the wrist, permitting it to connect and detach from an arm autonomously.
The hand’s fingers can bend in each instructions, permitting it to make use of a few of them to carry objects whereas the remaining perform as tiny legs. This design additionally expands the usefulness of the hand whereas it’s hooked up to a robotic arm. It might probably carry a number of objects directly with out twisting the arm round to reposition unused fingers.
The hand can also be significantly smaller than robots like Boston Dynamics’ Spot, which may freely locomote utilizing 4 legs. Spot has already been upgraded with its personal robotic arm and grasper, however with an articulated hand that operates independently, it could possibly be higher outfitted to discover or analyze areas Spot can’t squeeze into.