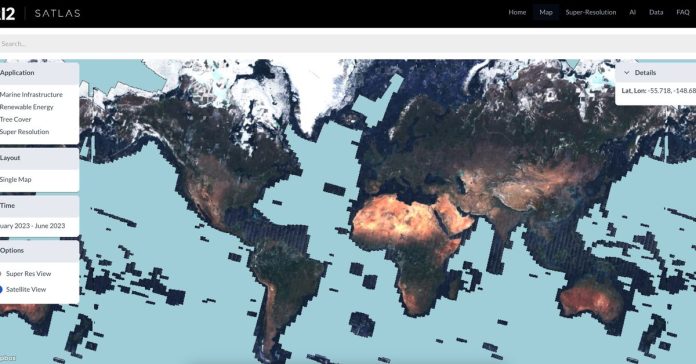
A primary-of-its-kind map of renewable vitality initiatives and tree protection around the globe launched at the moment, and it makes use of generative AI to basically sharpen photos taken from area. It’s all a part of a brand new device referred to as Satlas from the Allen Institute for AI, based by Microsoft co-founder Paul Allen.
The device, shared first with The Verge, makes use of satellite tv for pc imagery from the European House Company’s Sentinel-2 satellites. However these photos nonetheless give a fairly blurry view of the bottom. The repair? A characteristic referred to as “Tremendous-Decision.” Mainly, it makes use of deep studying fashions to fill in particulars, like what buildings may seem like, to generate high-resolution photos.
For now, Satlas focuses on renewable vitality initiatives and tree cowl around the globe. The information is up to date month-to-month and contains elements of the planet monitored by Sentinel-2. That features a lot of the world besides elements of Antarctica and open oceans removed from land.
It reveals photo voltaic farms and onshore and offshore wind generators. You can too use it to see how tree cover protection has modified over time. These are essential insights for policymakers attempting to satisfy local weather and different environmental targets. However there’s by no means been a device this expansive that’s free to the general public, in accordance with the Allen Institute.
That is additionally possible one of many first demonstrations of super-resolution in a world map, its builders say. To make certain, there are nonetheless just a few kinks to work out. Like different generative AI fashions, Satlas remains to be vulnerable to “hallucination.”
“You possibly can both name it hallucination or poor accuracy, however it was drawing buildings in humorous methods,” says Ani Kembhavi, senior director of pc imaginative and prescient on the Allen Institute. “Possibly the constructing is rectangular and the mannequin may suppose it’s trapezoidal or one thing.”
That is perhaps attributable to variations in structure from area to area that the mannequin isn’t nice at predicting. One other frequent hallucination is putting vehicles and vessels in locations the mannequin thinks they need to be primarily based on the pictures used to coach it.
To develop Satlas, the group on the Allen Institute needed to manually pour by means of satellite tv for pc photos to label 36,000 wind generators, 7,000 offshore platforms, 4,000 photo voltaic farms, and three,000 tree cowl cover percentages. That’s how they skilled the deep studying fashions to acknowledge these options on their very own. For super-resolution, they fed the fashions many low-resolution photos of the identical place taken at completely different instances. The mannequin makes use of these photos to foretell sub-pixel particulars within the high-resolution photos it generates.
The Allen Institute plans to broaden Satlas to supply other forms of maps, together with one that may determine what sorts of crops are planted internationally.
“Our aim was to type of create a basis mannequin for monitoring our planet,” Kembhavi says. “After which as soon as we construct this basis mannequin, fine-tune it for particular duties after which make these AI predictions out there to different scientists in order that they will research the results of local weather change and different phenomena which are taking place on the Earth.”